What is EV Power? EV Power is Changing the Future of Transportation
What is EV Power? EV Power is Changing the Future of Transportation
Blog Article
Share Now:
LinkedIn
Twitter
Facebook
Reddit
Pinterest

- Source: Images by Es_sarawuth
In the blink of an eye, the auto industry is changing from the old fuel engines to electric vehicles (EVs). Greatly fuelling this change is the power of EVs, which have a green, eco-friendly motor. If you are currently in the market for switching to electric vehicles, understanding how EV power works and the systems in its support is very important. This article presents the technical basics of EV power, charging types, turnover of EVs, and what their future might look like.
What is EV Power?
Simple as it may be, EV Power refers to the electrical energy that is facilitated by the motion of electric vehicles. Unlike cars that run on gasoline or diesel, using fossil fuels for energy production, EVs draw their power from electricity stored in batteries. This gaudy electric charge powers an electric motor to drive the car along. The power output of the motor is given in kilowatts (kW), while the battery storage unit is given in kilowatt-hours (kWh). All this means that the higher the kWh rating a battery has, the more miles it can go on one charge.
It starts with generation- the actual inputs of the electricity that come from various sources. This range includes renewable sources like solar or wind energy alongside traditional coal- or gas-fired power stations. Staying true to its name, the power grids distribute the electricity throughout charging stations and homes where EVs can be charged. From the charging stations to home charging, an onboard vehicle charger will modify the electricity received from the grid into a form acceptable to the EV battery. All this means that it is all about guaranteeing the efficient power supply that makes it usable to drive the EV.
Types of EV Charging
EV owners and prospective buyers need to know about the different types of EV charging, as this varies greatly in charge time depending on speed and connector. In general, EV charging can be broken down into three levels:
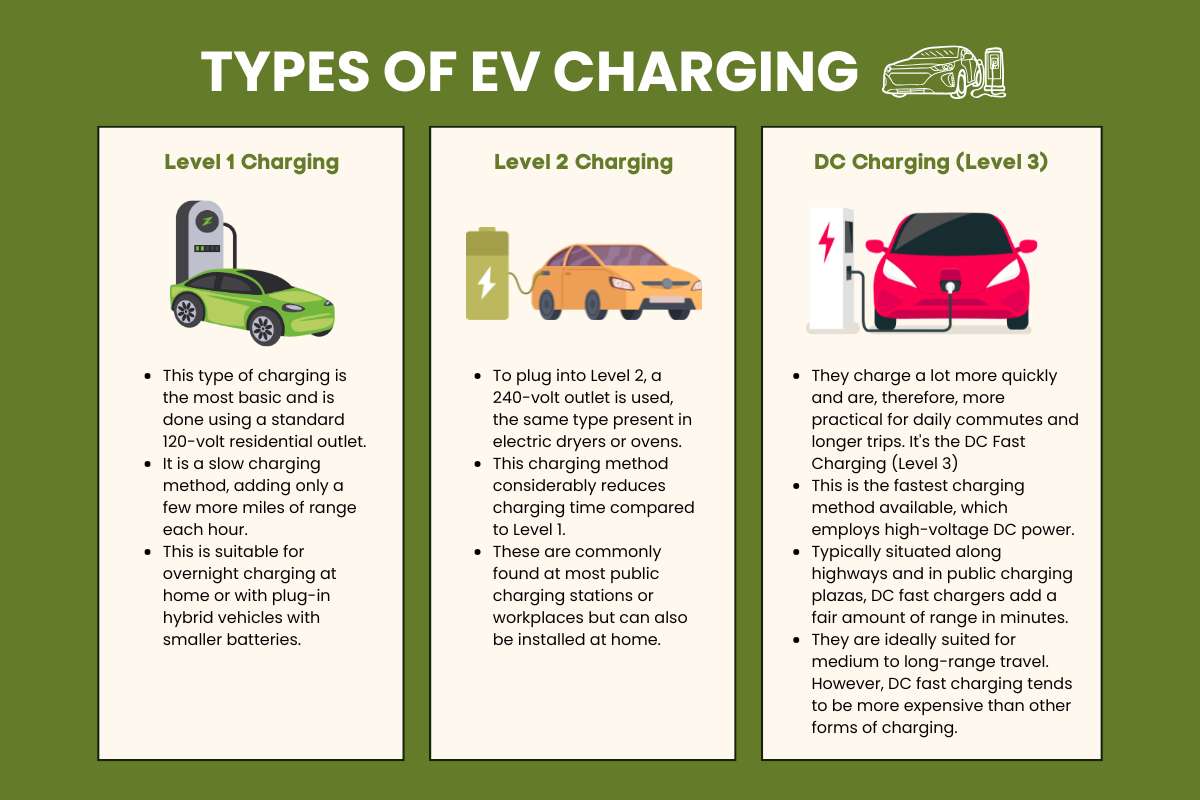
Level 1 Charging
- This type of charging is the most basic and is done using a standard 120-volt residential outlet.
- It is a slow charging method, adding only a few more miles of range each hour.
- This is suitable for overnight charging at home or with plug-in hybrid vehicles with a smaller battery.
Level 2 Charging
- To plug into Level 2, a 240-volt outlet is used, the same type present in electric dryers or ovens.
- This charging method considerably reduces charging time compared to Level 1.
- These are commonly found at most public charging stations or workplaces but can also be installed at home.
DC Charging (Level 3):
- They charge a lot more quickly and are, therefore, more practical for daily commutes and longer trips. It’s the DC Fast Charging (Level 3)
- This is the fastest charging method available, which employs high-voltage DC power.
- Typically situated along highways and in public charging plazas, DC fast chargers add a fair amount of range in minutes.
- They are ideally suited for medium to long-range travel. However, DC fast charging tends to be more expensive than other forms of charging.
Besides the levels, factors influencing charging speed include the connector used. Different manufacturers and charging networks use various types of connectors, many very distinctive: CHAdeMO, CCS, and others are plugged into the car directly. There are standardization efforts underway to solve the problem of getting various cars to use the same charging connections.
Charging Infrastructure Investment

Building a reliable charging infrastructure is about more than just establishing charging stations-there is the continued requirement for the stations to be reliable and user-friendly. The right locations, sufficiency of power capacity, and ease of payment should be the main factors to consider. Moreover, the grid itself is going to need upgrades to manage increased demand for power initiated by EV uptake.
Smart charging technology has become very vital indeed. Things like this manage when and how you change your electric vehicle. It prevents an overload of electrical distribution and is supposed to help with easing energy delivery. It thus plays the most important role in securing EV power sustenance for many years to come.
Benefits of EV Power and Charging Infrastructure
The shift to EV will include a variety of benefits to individuals in addition to benefits to the environment.

- Less Pollution: Electric vehicles do not pollute the air and will significantly improve the air quality by emitting no or very low amounts of greenhouse gases during their operation, especially in highly polluted areas like cities.
- Minimally Costly: Compared to gasoline, electric vehicles are less expensive and specifically have proven cost-effective by requiring less maintenance.
- Energy Independence: Electricity from many sources, including renewables, allows EVs to lessen independence on foreign oil and thus allow better energy security.
- Quiet: Electric motors are orderly operators compared to combustion engines, enhancing the driving experience and reducing noise pollution.
- Government Incentives: Various governments across the globe offer rebates, subsidies, and tax credits to assist in making EVs more affordable and to enhance charging infrastructure.
This heralds cleaner, more affordable, and sustainable transportation.
Future of EV Power
The EV power sector has the prospect of enhancing bright lights with the developing technology. This will include battery technology, improvement in infrastructure for charging, and smart grid integrations. With enhanced performance, upcoming batteries offer an extended driving range and shortened charge time, which further will render EVs affordable.
Inductive charging is also coming into the fold, providing lightweight, wireless charging. Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology allows EVs to be mobile power systems that transfer electricity back to grids, thus acting on balancing loads of consumption and providing stability and resistance to the grid.
The integration of EVs and smart grids is promising to further optimize energy consumption with improved balance on the supply and demand sides for a more efficient and sustainable future for EV power.
Conclusion
What is EV power? It is beyond just electricity that propels electric vehicles; it means an utter revolution in transportation, offering cleaner, greener, and often cheaper alternatives to conventional gasoline-powered vehicles. EVs use rechargeable batteries to store energy harnessed to run electric motors that propel the vehicle. EVs will emit much lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to their gasoline counterparts, even considering that electricity is generated from non-renewable sources. With technological advancements, future batteries will have better efficiencies, longer range, and shorter recharge times as charging infrastructure keeps developing. With this progress and with the clear environmental and economic advantages of electric vehicles, EVs will represent the future of transportation.